Maria Rosa Lorini and Memory Mwadziwana
A novel initiative to celebrate the International Day of the Girl Child took place in the vibrant city of Cape Town, South Africa, on 11th October. This was driven by a collective commitment to disseminate the importance of safe, wise and secure use of digital technologies, one of the corner stones of Work Package 9 (WP9) within the MIDEQ Hub funded by the UK government’s UKRI GCRF. This team is dedicated to harnessing the potential of digital tech to improve the lives of people and has dedicated much attention and care to discussing the side-effects of the digital world and to find ways to decrease any potential harms, especially when working with vulnerable groups.
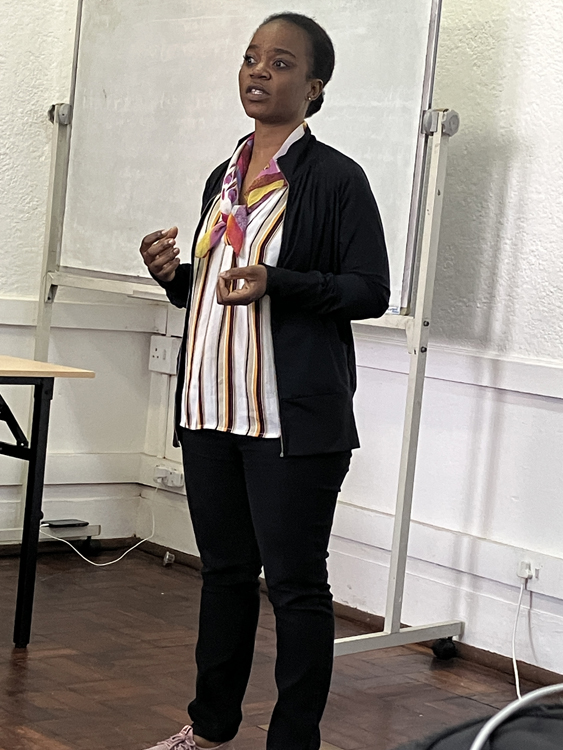
Five of the migrants living in South Africa and trained in digital skills through MIDEQ’s WP9, organised and managed an event that stands as a testimony to the importance given by people from many different backgrounds to the safe, wise and secure use of digital tech, and also witnesses the power of autonomous action and community engagement. The ‘Big Five’, as the activists called themselves in a comparison with the charismatic South African megafauna, took it upon themselves to participate in a school event dedicated to girls. This event took on added significance given the unique challenges faced by girls in the digital landscape, including issues of sexual harassment and trafficking, particularly within the migrant community. The school is situated in an area characterized by a significant concentration of migrants, and the teachers there are well-informed about the delicate issues associated with xenophobia and hate speech. Their stydents comprises girls from various nationalities, including Kenya, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. Notably, the facilitators, who hail from Zimbabwe and the Democratic Republic of Congo, were themselves also able to glean valuable insights from the small group conversations during the activities.
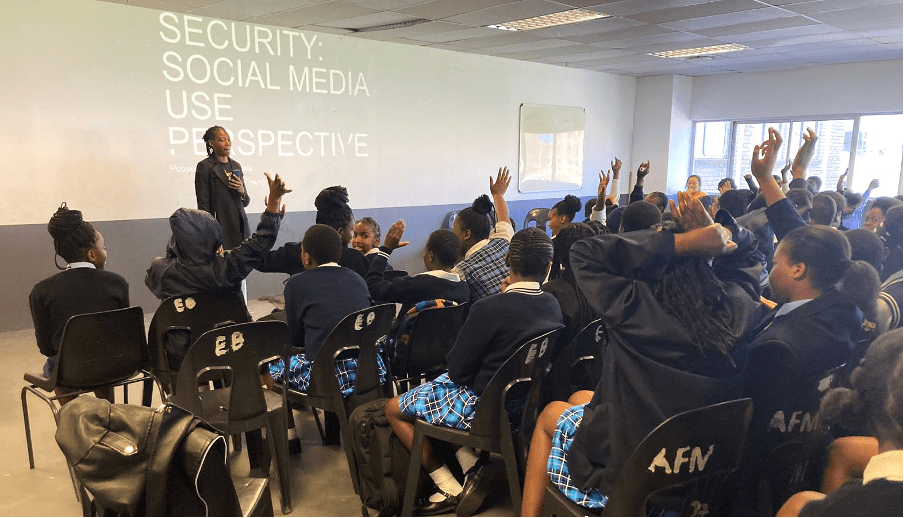
The autonomy and initiative of these migrants trained through WP9 shone through as they seized the opportunity to impart crucial knowledge on online safety and security. As facilitators, they valued the school and specifically the chance to contribute to an event focused on girls’ perspectives. This was just the right arena with a relevant audience to spread messages and initiate a conversation with both students and teachers on risky digital behaviours that are too often underestimated. Above all in marginalised areas affected by limited infrastructures and high inequalities, parents and teachers do not consider digital risks as a priority to worry about. Nevertheless, as the facilitators highlighted during their talks, more and more often technology is the conduit of sexual harassment initially online and soon afterwards in person.
To emphasize the importance of being cautious and discerning while online, the speakers posed a provocative question to the students, asking them who assists them at school. The young audience quickly responded, stating that they have friends. However, when a similar inquiry was made regarding social media, the students became uncertain and struggled to formulate their responses. Throughout the session, the facilitators carefully avoided sounding judgmental about common mistakes or limited knowledge of online risks and solutions. Instead, they tactfully encouraged students to reflect on aspects such as the potential for online tracking when sharing personal pictures of their daily activities.
These migrants are among the founders of the Fusion Avenue YouTube Channel – a collective of migrants living in South Africa dedicated to exploring cultures, ideas, and viewpoints with the goal to bridge gaps, celebrate differences, and find common ground. With the consent of the school, the facilitators created a video reportage of the event, and have posted this on their channel (click also on the image below).

Join us on this journey as we delve into the details of this inspiring initiative, exploring how these dedicated facilitators catalysed the attention of their young audience and left a mark on the students and teachers with whom they engaged. This is a story of empowerment, autonomy, and the boundless potential of collaboratiion that we would like to tell though their own voices.
Memory Mwadziwana, one of the facilitators, captured the essence of the day in this way
“Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to a recap of the extraordinary International Girls Day event! Ladies and gentlemen, this is Memory, reporting on the extraordinary International Girls Day event that took place on October 11th at the Purpose Finders School. It was a day that resonated with empowerment, education, and unity, leaving a profound impact on both the girls and the teachers who took part.
The day kicked off with a briefing by our dedicated organizers, laying the foundation for what would become a transformative experience at Purpose Finders School.
An emotional prayer permeated the air, symbolizing hope and unity and setting the tone for the day’s events. It was followed by a shout-out to the remarkable facilitators and organizers, including Fusion Avenue, Women African Weavers, DMS Ministry, and Purpose Finders School. Their unwavering dedication forged a sense of community, creating a collaborative atmosphere that would define the day.
The girls took centre stage, sharing poignant poems that transcended mere performance; they became acts of self-expression and empowerment. The bond between teachers and students strengthened as educators gained a newfound appreciation for the incredible talents of their charges.
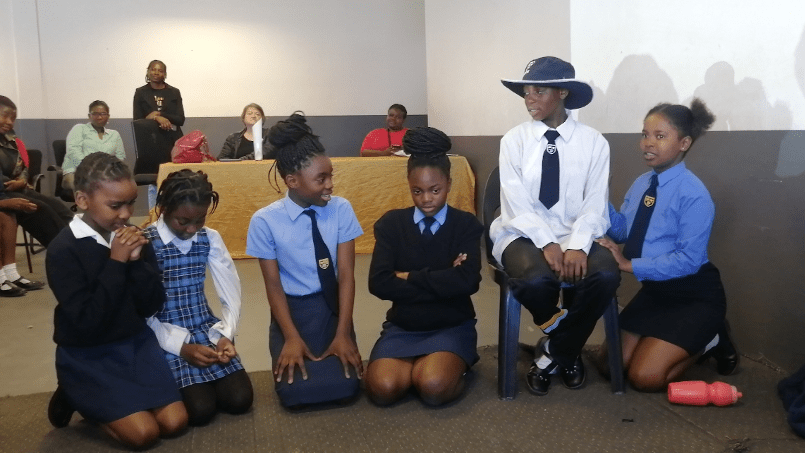

A highlight of the event was Pascal’s presentation on online safety and security. Trained by the MIDEQ Project, Pascal and her colleagues brought forth critical topics, including personal data exposure, digital harassment, hate speech, and online scams. In an age dominated by digital interactions, this knowledge proved invaluable.
Reiterating the importance of online safety, the event underscored the significance of being vigilant and informed in the digital world. Teachers expressed gratitude for the invaluable knowledge, and the girls left with newfound confidence.

Reporting from the Purpose Finders School, this is Memory, signing off with a heart full of inspiration and hope for the continued empowerment of young minds.”
At the end of the event, a debriefing session took place among the facilitators and the teachers who were keen to discuss further involvement of the ‘Big Five’ in this learning process, starting from themselves as educators.
From our side in MIDEQ WP9, we can only wish the Fusion Avenue team more successful events such as this!